Let’s say your banjo-obsessed buddy asks you to join him at the local Tuesday night bluegrass jam. Bluegrass. Sure, you’re aware of the term. You loved that George Clooney movie. You’ve got a couple verses of “Wagon Wheel” up your sleeve for wedding receptions. Plus, you’ve been wondering how Garrison Keillor suddenly got so good at the mandolin. Why not dive a little deeper?
As a newcomer to the strange pastime of standing in a circle with fiddles, banjos, and mandolins, you will be perfectly positioned to ask a really good question: “Where did all of these songs come from?” Your banjo friend might try to satisfy you by calling the songs “traditional,” but that’s just evading the question. Sure, some common tunes arrived in America on boats from Europe, and some of them were “collected” by folklorists like John and Alan Lomax who combed through rural America in the early 20th century, but the bigger-picture truth is that the bluegrass canon has been alive and evolving throughout its history. Even before bluegrass’s inception in the 1940s, the story of folk music in the 20th century is one of surprising re-discovery, unorthodox re-interpretation, and, yes, the addition of songs that happen to be brand new. Right up there alongside the other great writers and re-interpreters — A.P. Carter, Bill Monroe, the Stanley Brothers, and many others — there’s a whipper-snapper (by “traditional” music standards) named Tim O’Brien.
Tim’s band, Hot Rize, emerged in the late ’70s as part of a neo-traditional reaction to New Grass Revival and David Grisman’s no-holds-barred hippie bluegrass boom of the early ’70s. There was a back-to-basics element to Hot Rize’s chemistry — led by O’Brien’s distinctive tenor and mandolin playing — but bassist Nick Forster played an electric bass, banjo player Pete Wernick occasionally played through a trippy phase-shifter effect, and they all wore obnoxiously ugly ties with their formal wear. (Traditional Ties was one tongue-in-cheek album title.) In other words, in a world of stiff suits and tall Stetsons, they injected a playfulness that both revitalized the tradition and reminded it not to take itself too seriously. In that way, they weren’t a reaction to New Grass Revival so much as their fraternal twin. Both bands effectively proved the point: Long-haired kids can play their own kind of bluegrass.
Tim’s original songs “Nellie Cane” and “Ninety Nine Years” share the rare double distinction of being staples of many local jams and also popular covers in the repertoires of Phish and the Punch Brothers, respectively. He’s also re-energized old songs like “Blue Night,” “Pretty Fair Maid,” and “Look Down that Lonesome Road,” bringing them and many others into popular bluegrass rotation.
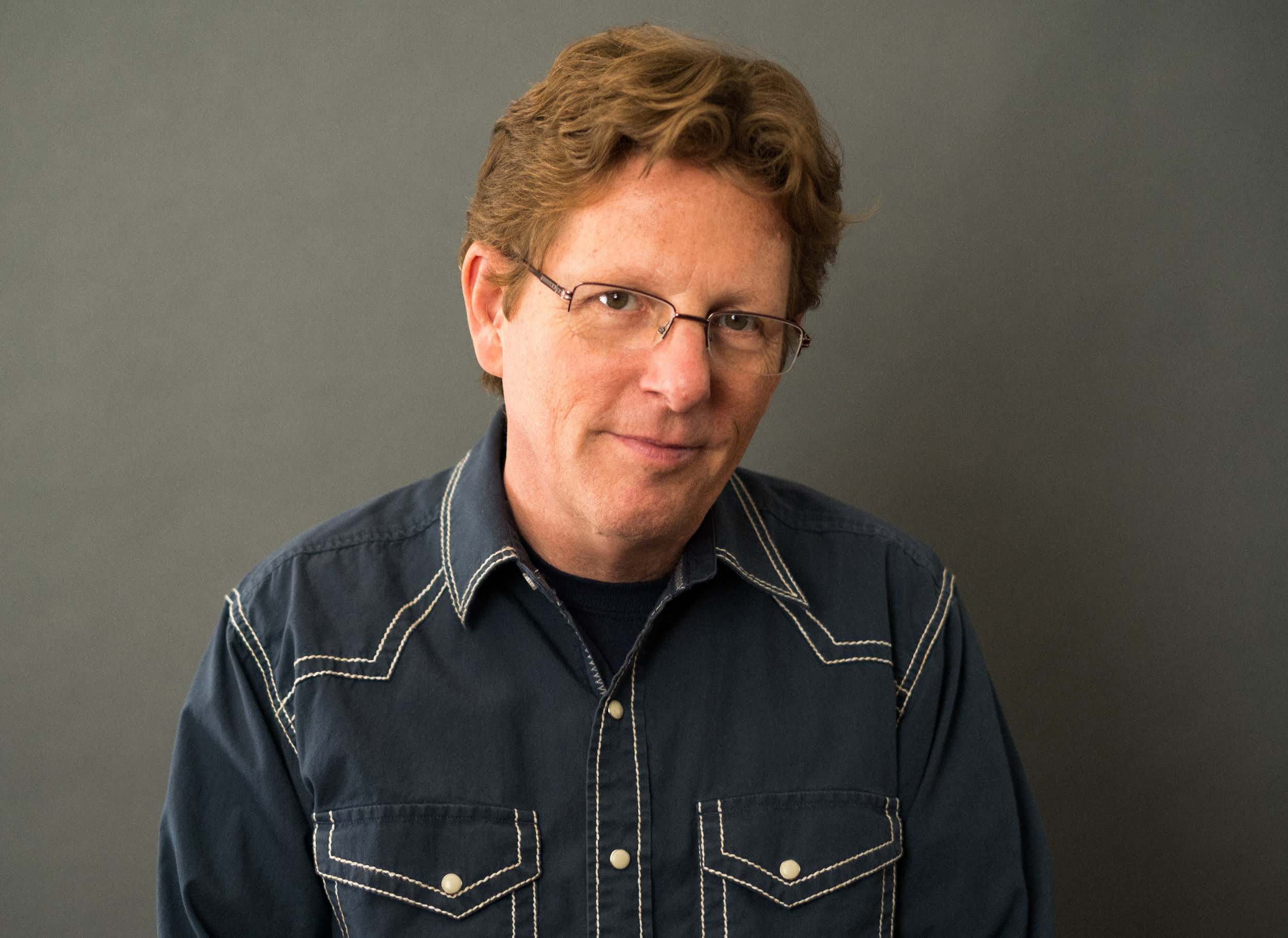
Before all that, O’Brien was just a kid from West Virginia listening to the Beatles on the radio and playing wedding gigs with his talented sister, Mollie O’Brien. This month, he released a record, Where the River Meets the Road, that returns him to his West Virginia roots. True to form, he uses the opportunity to try his hand at old gems like “Little Annie” and to bring to life surprising re-interpretations of other West Virginians’ songs, like Bill Withers’ “Grandma’s Hands.” We talked about the new record as well as his many decades spent nudging the folk tradition forward.
The band on Where the River Meets the Road is killer. They really move together like a tight band, rather than just background studio musicians. Some of them are familiar folks from the bluegrass world like Stuart Duncan and Noam Pikelny. How’d you end up incorporating Chris Stapleton?
I’ve known Chris for a good while. When he first moved to Nashville, Bryan Sutton was hired to produce demos of his. I went and played and sang on his demos, and I was really impressed. We wrote together a little bit, messed around. We stayed in touch. He sang on a record I made called Chicken and Egg. I was really pleased he was able to sing on this one.
That’s a great duet. Your voices are totally different, but the harmony is kind of striking. It really works.
He came in there and nailed that thing. I have to say, that track was good before he sang. You know how it can get in the studio. It’s pretty mellow listening to the same track over and over. Then he came in, started singing, and we all shot up straight in our chairs. Our spines straightened and our hair stood up on the back of our necks. I said, “Yeah, more of that!” It was really wonderful.
I saw on your schedule that you’re headed to Wheeling, West Virginia, tonight.
Yeah, that’s right. I’m playing my hometown tonight. It’s really exciting and terrifying at the same time. I haven’t played there in so long, and I think most of the people who bought tickets in advance are friends of mine, so you’re kind of on display. But I’m excited about seeing the old hometown.
Have you spent much time there since you left home many years ago?
No. You know, my dad died in 2011, and my mom had died before. I have a few cousins there, but I’m not close to them. I’ve only just sort of passed through a couple of times. I played with the Wheeling Symphony a couple of years ago and that was fun. My sister and her husband and my partner Jan and I sang.
Wheeling has a symphony?
Wheeling was the biggest city in the state for a long time. It was the only symphony in the state before they ever had one in Charleston. Yeah, Wheeling was a rich town with a steel mill at one point. People dressed in finery, you know. It’s a faded town now, but it has surprising culture. [Laughs]
And it had a great radio station that you grew up listening to, right? WVA?
WVA was a great resource. I was into pop music and stuff at the time, but WVA was a place you could actually see live performers on a Saturday night. I enjoyed listening to the radio, as well, but I liked going down to the Saturday night show and seeing the pros play their guitars.
But you were just a kid mostly listening to pop radio and Beatles records. So, in other words, you weren’t from a traditional music family on an inevitable path toward a folk career?
No. Not at all. My parents loved music, but it was just on the sidelines. They liked the music of their era — Glen Miller and Benny Goodman and stuff like that. When my sister and I got into music, they encouraged us. They tried to steer us toward a well-rounded experience growing up, so we could choose what we wanted to do.
Did you and Mollie sing together and learn from each other growing up?
Well, she was playing the piano and I started playing guitar. By the time she was in high school, she was studying voice there, so, yeah, we would get some little gigs — school plays, different things. We would play at weddings, sing a few Peter, Paul, & Mary songs, Beatles songs, or whatever.
Then you left college to move west and pursue music. Did your parents think you were crazy?
Well, I was the youngest of five. Being the youngest, my parents cut me a lot of slack, I’d say. They had been through it with the rest of them. Also, you know, I was determined. They wanted me to stay in college, but I just wasn’t going to respond. So they said okay. I think they were holding their breath for about three years. Then I put out a record on a little label — I think it was ’77 or ’78 — and that’s when they finally said, “Oh, maybe this will lead to something.” They developed a more open mind. Then my parents became big fans of whatever I was doing and supported it. So it was a gradual thing, kind of a wait and see. They lightly steered me, but they knew they couldn’t do the final job, you know? I’m lucky I had that background with them.
So after growing up in West Virginia, you moved out west to Colorado to get your career started. Why did you feel like you had to leave the south to play bluegrass music?
My dad said, “You just want to go as far away as you can, don’t you?” I said, “Well, sort of.” [Laughs] Really, I was going out there because I loved the weather and the scenery, the lifestyle out west. I thought in a ski area, maybe I could play music and ski — both things I was excited about. So I went to Jackson Hole. Some other friends that had worked at summer camp with me were going to spend a winter there, so I went out and joined them and scuffled around for the winter. I ended up looking for a more active music scene and I ended up in Boulder. I guess I could’ve moved to a college town in West Virginia, but I wanted to see the rest of the country.
It’s funny — when I sing the song, “High Flying Bird,” from this record, I realize it’s symbolic of what I wanted to do when I was young. I wanted to get the heck out of there. I didn’t want to be rooted and tied down in West Virginia. I wanted to see the rest of the country, the rest of the world. And I didn’t realize that song was from West Virginia until now. You get away and you find perspective on where you left. You can see it from a longer view. The music provided a connection to West Virginia, as well as my family, so I kept going back. I realized it was a valuable base to have started from, and I continue to value that.
What is it that’s made you interested in reconnecting with your West Virginia heritage? Why now?
I feel like I’ve been given a gift of this music and this background. I got involved with the West Virginia Music Hall of Fame when they wanted to start that about 12 years ago. Meeting all these people as they come through to be inducted was really wonderful. You learn that a lot of people you knew about and music that you’d heard came from West Virginia.
Until I heard your record, I had no idea Bill Withers was from West Virginia.
Yeah, and that’s the thing. Part of the aim of the Hall of Fame is to connect those dots. We’re doing it for the public, but as it turns out, the members of the board and the members of the Hall of Fame are learning about the rest of the scene and connecting dots themselves. I think why I did this project now is, well, I needed to put a record together! [Laughs] I originally wanted to do a record of all original material, but I didn’t think I could pull that off for another year. I’d been thinking about a West Virginia record for a while, and I didn’t realize how much work I’d already done organizing it, making lists of songs, brainstorming on it. I’d already done a lot of that. So it came together really fast. It felt right.
One big part of your story is that you’ve made so many different types of music, so many types of records over the past nearly four decades. Do you have to keep exposing yourself to new songs and new sounds to keep your ideas fresh? How do you do that?
You just keep looking. You go to the record store. Nowadays, I get online — YouTube or Spotify. Then back to my own old record collection. My huge CD wall. Every year, I clean a lot of stuff out of it, give it away, put it in the free box at the Station Inn or something. Then there’s a lot of stuff that always stays there — the first generation of bluegrass masters, or the Lomax field recordings, or classic songwriters like Randy Newman or whatever. Then my friends around me are always writing new stuff, and I’m trying to keep up with their stuff. It’s a constant search, and I always feel the need to refresh the palate. But it’s funny — even by going back to the same stuff you’d passed over, you’ll hear new things and learn. So I’m always combing. Part of the week’s work is to comb for new music.
I like that — it’s part of the week’s job. It’s what you do when you wake up. Reminds me of the first time I saw you solo, at Grey Fox in 2012, when you did a solo guitar tribute to Doc Watson. I’m a North Carolinian and I know Doc’s stuff pretty well, but you put a new stamp on those tunes. It was like rediscovering Doc. So, for me, it was a sort of revelation, but I heard a guy next to me say, “Wish he’d brought his mandolin …” I can imagine for you that must be frustrating. Do you have to put effort into not being pigeonholed?
Yeah, you do get pigeonholed in bluegrass. I think back when I was starting, if you did bluegrass, you couldn’t do anything else. People wrote you off. When Pete Wernick called me [in 1978] and said, “Hey, why don’t we get a band together?” — our solo records were both coming out around the same time in ’78 — I said, “Yeah, that would be great.” I told him I wanted to play some traditional bluegrass, for sure, but I also wanted to do some country music and different things. I asked him if he played dobro so we could get away from the traditional thing.
Nowadays, the rock ‘n’ roll and country players, even the jazz players, are respectful of bluegrass. They understand it’s a training ground, that there’s a certain amount of woodshedding you have to do to even try to play bluegrass. So, yeah, I didn’t want to be pigeonholed. But I am pigeonholed. I’m always referred to as a bluegrass artist — and I’m glad to have a handle to carry it around on. Bluegrass music is Bill Monroe’s music, but then the bluegrass audience is a separate thing. There’s the genre as defined by the history, the classic examples. Then there’s the genre as defined by the audience — though it may only be a small part of what that audience listens to. So, in a way, I’m lucky to have been labeled a bluegrass artist while still sneaking in this other stuff. If I play something on acoustic instruments, they tend to accept it. Bluegrass fans are a very tenacious, very loyal bunch. They keep giving you another chance.
Can’t they be a pretty judgmental bunch, too?
I’m sure there’s judgmental stuff going on, but I don’t really look for that or worry too much about that. I just go my way and hope things will work out. And they have. I tried to get on a major label — I sort of glanced at the big time there. It didn’t take. I thought maybe I’d get the big publicity for a while and then I’d be on my way. Instead, I dug into the trenches of the folk and bluegrass worlds and developed an audience slowly but surely. You’re a product of what you do, so if my output has been eclectic, the audience that has remained has been willing to accept that. There’s enough of them out there to make a career.
Back in the Hot Rize days, and also what you do now, your music was right on that line between the traditional and the progressive — or neo-traditionalist, as people called Hot Rize. Did you ever feel any tension between those two camps? Or was the general attitude different in Colorado?
With Hot Rize, it was interesting. West of the Mississippi, we represented a traditional bluegrass band, but east of the Mississippi, we were these wild card guys. Our hair was too big and our ties were wrong and we had an electric bass.
But you guys had a sense of humor about it, too.
Yeah, we did. I mean, you’ve probably been at a bluegrass jam where people play a tune and, when it’s done someone, will say, “Well, that’s not bluegrass,” and everyone will laugh. Bluegrassers are always referring to their relationship with Bill Monroe’s music. They’re always measuring that. It’s part of our thing.
Sort of a self-conscious conversation we’re always having.
Yeah. And there is a tension. I’ll say this: There are a couple of places where we couldn’t get booked because Pete [Wernick] is Jewish. But, like I said, we took it where we could. Luckily, we came along at a time when people like New Grass Revival and David Grisman had broken a lot of ground. There was a hippie element that supported an alternative to the music. We were on a wave that was returning back to a traditional sound — the Johnson Mountain Boys, Nashville Bluegrass Band, Doyle Lawson & Quicksilver were starting out at about the same time. They were hip and innovative in the way they were presenting traditional music, but they weren’t breaking the walls down like New Grass Revival did. This was viewed by a lot of people as a refreshing return to form. We enjoyed that. You know, we tried to play the kind of no-boundaries music when we started, and it just didn’t work out. Charles [Sawtelle] was playing bass at first, and we had a different guitarist. When Charles started playing guitar, he was much better at the traditional stuff. And we felt better playing it. You’ve just got to find your feet in whatever situation you’re in. That seemed to be the way to go, so we kept going there.
Since then there have been many ups and downs in terms of bluegrass’s broader popularity, the general awareness among the public. Is there anything that surprises you now about what the scene is like or feels particularly different about the 2017 bluegrass world?
The biggest draws in bluegrass now are the jam bands. Again, if you defined it in terms of Bill Monroe’s music, they’re not bluegrass. But they’re playing banjo and bluegrass and they’ve got a lot of attention. There’s a crowd that will get interested in that and look behind it for their influences. They might get into Widespread Panic or the Grateful Dead — or they might go to Doc Watson and the people that he learned from. The thing about bluegrass — even with the ebbs and flows of it — it’s always been growing. With O Brother, Where Art Thou, or with Alison Krauss crossing over into country, or with String Cheese Incident becoming a big draw — there might be a surge related to those things. But mostly the genre grows slowly like a tree. It’s healthy. The roots are growing, as well as the branches.
From those days starting out with Hot Rize in ’78, it just seems to keep growing. That’s the overall trend. Young kids are going back to the old stuff and remaking it. Even if you do something that’s been done before, your version of it will appeal to someone in a new way. It’s heartwarming to see it. Evolution is part of the definition of tradition. Each musician is a link in the chain and, whether you like it or not, you’re part of a tradition. You’re not going to do it exactly like the old folks did it, and you’re not going to do something completely original. You might as well get used to it.
In the same vein, you’re circling back to Wheeling tonight.
Yeah, it’s really exciting. I’m playing a little restaurant bar! [Laughs] Almost everyone there will be my friend, so that’s a little intimidating. But it’ll be fun. I just want to go out and walk the streets a little bit.